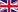
The principle is simple: tap water flows through a stainless steel tank containing a mixture of special resins and comes out desalinated and demineralised. Ion exchange takes place inside, whereby the higher the charge and the smaller the ion radius, the more strongly the ions are bound to the ion exchange resins.
Ion exchange is the reversible process of exchanging desired ions for undesired ions between a solid and a liquid material. In applications for pure or ultrapure water, the solid material is usually styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer ion exchange resins and the liquid material is water.
For example: When water containing sodium chloride flows over and through the ion exchange resins, sodium is exchanged for hydrogen, while chloride ions are exchanged for hydroxide ions. Hydrogen and hydroxide ions then form the water molecule.
Ion exchanger cartridges
Easy to use, reliable and environmentally friendly in their function, these devices produce demineralised water by means of ion exchange. The scope of supply usually includes a conductivity meter, a hose connection set with quick-release couplings in the appropriate size and a filter cartridge.
In order to be able to call up optimum performance parameters from our new generation of metalworking fluids, such as increased tool life, reduced tool and seal wear, cleanliness and freedom from limescale of the machining unit and the interior surfaces of the machine tool, clear visibility through its viewing window and prevention of corrosion due to salts in the raw water, it is absolutely essential that the make-up water is fully desalinated.
The dpi coolant solutions do not need to be post-treated to prevent foaming. They could also work without raw water treatment, but then they would by far not reach the maximum performance parameters as with desalinated water. Some corrosion phenomena caused by desalination (chlorides, fluorides, sulphates, phosphates, calcium, etc.) during the life of the solution and increased conductivity cannot be prevented without full desalination.
We will be happy to name high-performance suppliers of such systems in your area on request.
Conductivity measuring device – standard
Measuring device for checking the conductivity (µS) in the raw water inlet after the filter unit. Power is supplied via a 220V/50Hz earthed plug cable and a connection to the ion exchanger via a push/pull quick-release connector (or 1 1/4" threaded connection). The unit is completely pre-assembled and ready for connection and is checked for function at the factory.
Conductivity measuring device with automatic switch-off
Wherever it cannot be guaranteed that the existing conductivity display on the ion exchanger cartridge is monitored and controlled by the operating personnel, it is advisable to install a conductivity meter with automatic switch-off device. This prevents the ion exchanger cartridge from being "overrun" and uncontrolled (salinisation) and thus corrosion of the machines and their tools.
Conductivity measuring device with automatic switch-off and 3/4" (WATER-STOP) valve for the raw water inlet, power supply via 220V/50Hz with safety plug cable and a connection to the ion exchanger via a push/pull quick release (or 1 1/4" threaded connection).